The breathing/Anesthesia Circuit is the lifeline between the patient and the anesthesia workstation/Ventilator. It consists of various combinations of interfaces, enabling the delivery of medical gases to patients in a consistent and highly regulated manner. We provide a wide range of devices to equip you with tools to deliver the outcome for the patients.
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
● Tube types: Corrugated, Expandable, Smoothbore, Coaxial, Duo limbo.
● Customized length available,1.6m,1.8m, 2m,3m,3.6m,etc.
● Optional accessories: Extra Limb, Catheter Mount, Hook, Breathing bag, HMEF, Anesthesia Mask, etc.
● Size: Adult 22mm, Pediatric 15mm, Neonatal 10mm.
|
Item Number |
Description |
Diagram |
|
bc-160c |
Breathing Circuit Corrugated 160cm |
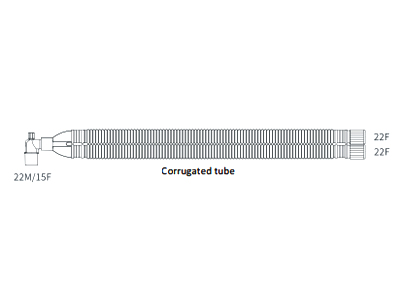 |
|
bc-160c-2w |
Breathing Circuit Corrugated 160cm with 2 Water Traps |
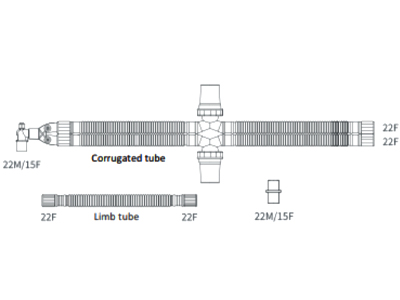 |
|
bc-160e |
Breathing Circuit Extendable 160cm |
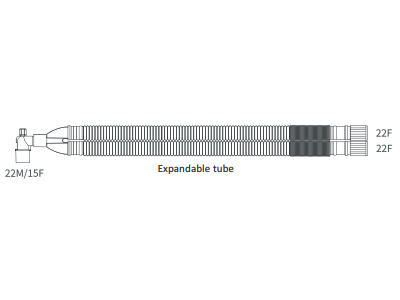 |
|
bc-160s |
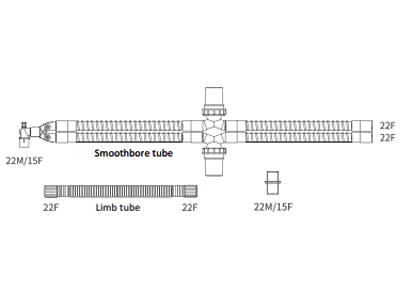
Breathing Circuit Smoothbore 160cm |
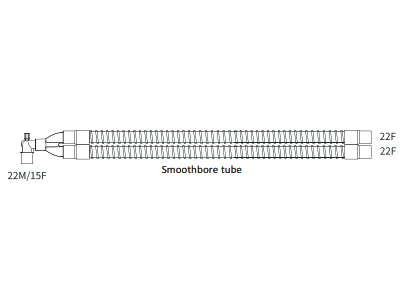 |
|
bc-160s-2w |
Breathing Circuit Smoothbore 160cm with 2 Water Traps |
 |
|
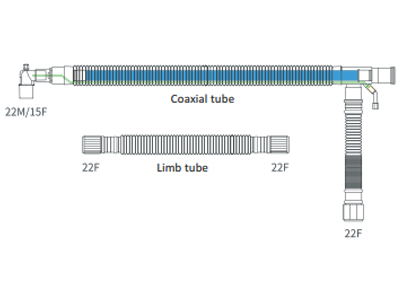
bc-180cx |
Breathing Circuit Coaxial 180cm |
 |
|
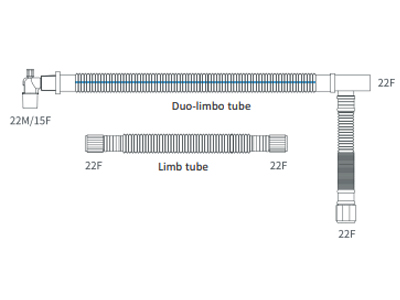
bc-180du |
Breathing Circuit Duo-Limbo 180cm |
 |
|
Customized length available,1.6m,1.8m, 2m,3m,3.6m, etc |
||





Overview of Silicone Reservoirs Silicone reservoirs are widely used in various industries for storing liquids due to their flexibility, chemical stability, and temperature resistance. They are common ...
View MoreRelationship Between the Ventilator and the Breathing Circuit The breathing circuit functions as the physical connection between a ventilator and a patient’s airway, enabling controlled delivery and r...
View MoreClinical Context of Uterine Tamponade Balloons in Prolonged Use Uterine tamponade balloons are widely applied in obstetric care to manage postpartum hemorrhage and other conditions involving excessive...
View More1.What is a Breathing/Anesthesia Circuit and How Does it Function?
A breathing/anesthesia circuit is a critical medical system that serves as the primary interface between a patient and the anesthesia workstation or ventilator during surgery or mechanical ventilation. This circuit ensures that medical gases, including oxygen and anesthetic agents, are delivered to the patient in a highly regulated and consistent manner. Its primary function is to maintain an open airway, deliver anesthesia, remove exhaled gases, and manage the patient’s breathing when they are unable to do so independently.
The anesthesia circuit is often described as the "lifeline" during surgical procedures because any malfunction in the system can directly impact the patient's ability to breathe and receive essential gases. These circuits typically consist of different components, including tubing, valves, connectors, and filters. Together, they control the flow, pressure, and composition of gases that enter and exit the patient’s lungs.
The circuit plays a key role in maintaining the right balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood, which is vital for the patient's health and safety during anesthesia. It also enables anesthesiologists to control the depth of anesthesia by adjusting the concentration of anesthetic gases. Modern circuits are designed with advanced features that allow medical professionals to easily monitor and adjust ventilation parameters, thus providing a safe and reliable tool for patient management. The choice of the right circuit is essential as it must match the patient's physiological needs and clinical setting, ranging from the operating room to intensive care units.
2.Different Tube Types and Their Significance
Breathing circuits are not one-size-fits-all; they come in a variety of tube types designed to meet specific patient needs and clinical environments. Each type of tubing offers unique benefits in terms of flexibility, airflow resistance, and the ability to retain heat and moisture, which are crucial for patient comfort and safety.
Corrugated tubing: This type of tube is characterized by its ribbed and flexible design, which prevents it from kinking or collapsing. Corrugated tubes are often used in situations where the circuit needs to be manipulated frequently, such as in operating rooms or intensive care settings. Their flexibility allows easy positioning around the patient, reducing the risk of airflow obstructions, which can be critical during long surgeries or in pediatric and neonatal care.
Expandable tubing: Expandable tubing is designed to offer variable lengths, providing better adaptability to different setups and patient needs. This flexibility is especially useful in environments where space or patient positioning might change, allowing medical professionals to customize the length of the tubing without needing to switch circuits. This can enhance workflow efficiency and reduce the need for additional equipment.
Smoothbore tubing: Unlike corrugated tubes, smoothbore tubing has a sleek internal surface, which minimizes airflow resistance and turbulence. This makes it ideal for situations where high-flow ventilation is required or where gas delivery needs to be as efficient as possible. The smooth interior also reduces the risk of moisture buildup and bacterial contamination, enhancing patient safety and the hygiene of the breathing system.
Coaxial and Duo limbo tubing: Coaxial and Duo limbo systems are more sophisticated types of tubing, where both the inspiratory and expiratory gases are handled within a single tube. This design reduces clutter in the operating room or ICU and helps maintain heat and moisture within the circuit. The added benefit of heat retention is particularly important for long surgeries or for patients with respiratory conditions, as it prevents the cooling of inspired gases, which can reduce patient comfort and complicate recovery.
3.Customization and Additional Accessories
In modern medical practice, customization of medical devices is essential to accommodate the diverse needs of patients. This is particularly true for breathing circuits, where customization can significantly enhance the efficiency, comfort, and safety of patient care. Breathing circuits can be tailored in terms of their length, size, and accessories, providing flexibility for a wide range of applications.
Customized Lengths: The length of the breathing circuit can vary based on the type of procedure and the patient’s position. Standard lengths include 1.6 meters, 1.8 meters, 2 meters, 3 meters, and 3.6 meters, though circuits can also be customized beyond these lengths. Longer circuits may be necessary in large operating rooms where the anesthesia machine is situated far from the patient or when additional space is needed to prevent circuit kinking. Conversely, shorter circuits can reduce dead space and improve the accuracy of gas delivery in smaller patients, such as neonates or infants, ensuring they receive precise volumes of oxygen and anesthetic agents.
Optional Accessories: Accessories play a vital role in enhancing the functionality of breathing circuits. For example, adding an extra limb allows for additional components such as humidifiers or filters to be incorporated without compromising the integrity of the circuit. Catheter mounts are useful for stabilizing the circuit, particularly during long procedures where frequent movement might cause disconnection. The breathing bag is an essential accessory that enables manual ventilation in case of emergencies, allowing healthcare providers to control the patient's breathing manually. Other important accessories include heat and moisture exchange filters (HMEF), which trap moisture and heat from the patient’s exhalation, returning it during inspiration to keep the airways humidified, thus preventing drying out of the airway mucosa. Anesthesia masks, tailored for different age groups and facial shapes, provide a secure and comfortable seal, ensuring effective gas delivery.
Size Options: Breathing circuits come in different sizes to cater to the needs of adults, pediatric patients, and neonates. Adult circuits typically use a 22mm diameter, which provides adequate airflow for larger lung volumes, while pediatric circuits use a 15mm diameter to suit smaller patients with lower tidal volumes. Neonatal circuits, which are even more delicate, come in a 10mm diameter, specifically designed to deliver small, precise volumes of gas, avoiding over-ventilation, which can be harmful to these vulnerable patients.